Prevention of Intraventricular Hemorrhage in the Neonatal Population
Prevention of Intraventricular Hemorrhage in the Neonatal Population
Purpose: To educate and inform about Intraventricular Hemorrhage (IVH) in the neonatal population.
Course: NURS 417 - Nursing Informatics
School of Nursing, Old Dominion University
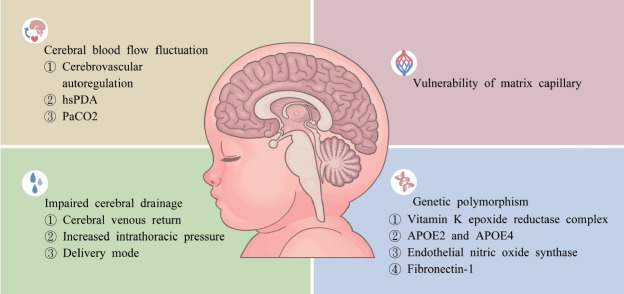
According to the Johns Hopkins Medicine (2020), Intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) of the newborn is bleeding into the fluid-filled areas, or ventricles, surrounded by the brain. The condition is most often seen in premature babies, and the smaller and more premature the infant, the higher the risk for IVH. This is because blood vessels in the brain of premature infants are not yet fully developed and are extremely fragile. IVH is rarely present at birth, and if it occurs, it will usually be in the first several days of life.
Antenatal: administering tocolytics (such as magnesium sulfate) & corticosteroids reduces RDS and shortens required duration of mechanical ventilation.
Perinatal: delayed cord clamping greater than 30 seconds or umbilical cord milking if baby is in distress and resuscitation efforts need to be made.
Postnatal: using indomethacin or IV Acetaminophen to assist in closing the Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA), surgical ligation of PDA, bundling care which includes supine midline with a neutral head positioning, raising head of bed 10-30 degrees to prevent head down position, avoiding stimulation & endotracheal suctioning, & providing intervention for pain/stress relief in the form of a pacifier, oral breast milk, or sucrose.
Honnorat, M., Plaisant, F., Serret-Larmande, A., Claris, O., & Butin, M. (2023). Neurodevelopmental Outcome at Two Years for Preterm Infants With Intraventricular Hemorrhage: A Case-Control Study. Pediatric neurology, 141, 52–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2023.01.013
Intraventricular hemorrhage. Johns Hopkins Medicine. (2020, July 20). https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/intraventricular-hemorrhage#:~:text=What%20is%20intraventricular%20hemorrhage%3F,higher%20the%20risk%20for%20IVH
Rees, P., Callan, C., Chadda, K. R., Vaal, M., Diviney, J., Sabti, S., Harnden, F., Gardiner, J., Battersby, C., Gale, C., & Sutcliffe, A. (2022). Preterm Brain Injury and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes: A Meta-analysis. Pediatrics, 150(6), e2022057442. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2022-057442
Tsao, P.-C. (2023, March 15). Pathogenesis and prevention of intraventricular hemorrhage in preterm infants. Journal of Korean Neurosurgical Society. https://doi.org/10.3340%2Fjkns.2022.0288
“Neurodevelopmental impairment was defined as cerebral palsy, hearing deficiency, visual impairment, or developmental delay. Multivariate analysis was used to identify whether high-grade IVH was an independent risk factor for neurodevelopmental impairment“ (Honnorat, et al., 2023, para. 3).
I am currently a Senior in the School of Nursing at Old Dominion University in Norfolk, VA. I am studying Nursing Informatics (NURS 417) under Dr. Lynn Wiles and Mrs. Leanne Stone.
Website: https://www.odu.edu/nursing
I work full time as a Registered Nurse in a Level III Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU). I have certifications in Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) and STABLE. In the NICU, neonates are often diagnosed with IVH. Evidence-based practice will not only help to lower the rates of IVH occurrences within the NICU, but it will also provide better outcomes for the future development of neonates.

Student Name: De’Saun Bruce, RN
