Phishing
Phishing
- Phishing is the way that criminals steal your personal information over the internet.
- How do they do it? By pretending to be a legitimate (real) business and asking you for information or stealing your password.
- In email - did you ever get an email from someone you do not know? Or from a business that is trying to give you something for free?
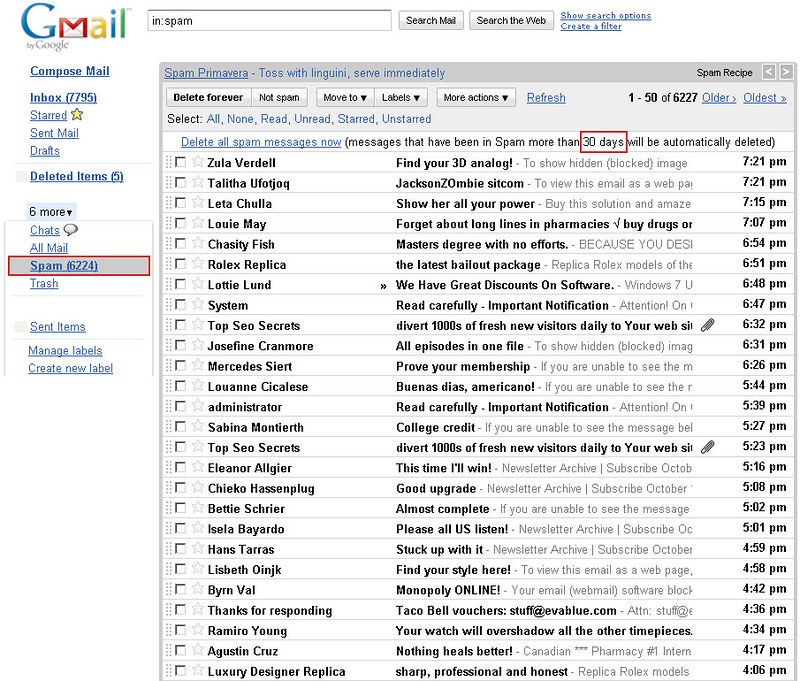
Spam inbox example:
Fake Amazon phishing email: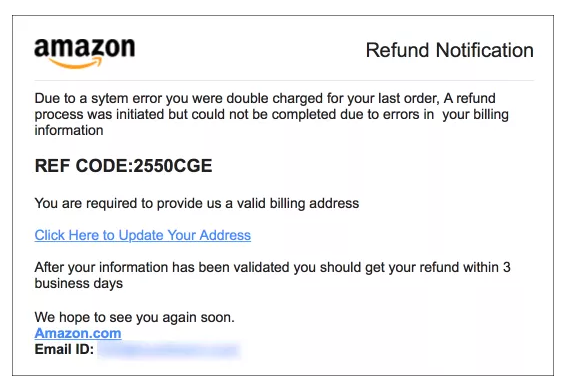
Fake bank phishing email:

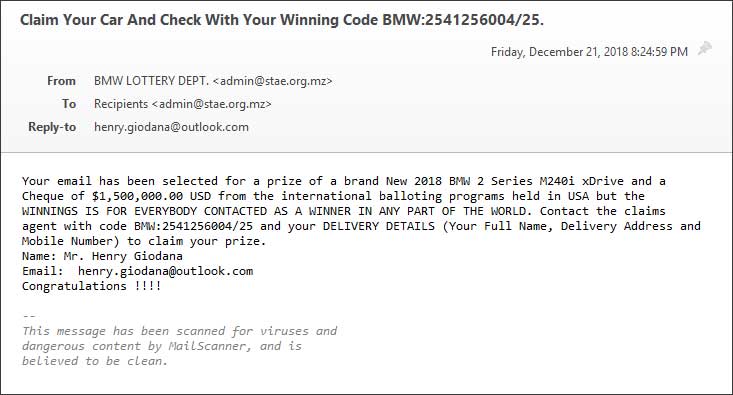
Lottery phishing scam:
- Do not email personal or financial information.
- Do not click on links in emails or reply to suspicious emails. Independently open a browser and type in the website address. That way, you control what sites you visit. Do not let a phisher direct you to a false site.
- Only provide personal or financial information through an organization's website if you typed in the web address yourself and you see signals that the site is secure, like a url that begins with https (the "s" stands for secure).
- Be very cautious about opening attachments and downloading files from emails, regardless of who sent them. These files can contain viruses or other malware that can weaken your computer's security.
- Be cautious about email messages that come from people or place you do not know. Scammers sometimes use mail or contact lists that are not protected - be sure to know who you are getting emails from.
- Be cautious of messages with no subject, or messages that are too general or strange for the person sending the email. If you think that a friend did not send the message, email them in a separate message and ask. Sometimes email address can be stolen by scammers.