Lymphatic System
Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system is made up of several organs plus a set of tubes that parallel the circulatory system but carry fluid in only one direction. This fluid is intercellular and is in part fluid lost through capillaries. The system returns this fluid to the circulatory system. On the way it passes through lymph nodes where the immune system can detect evidence of pathogens.
1. Lymph nodes – “bean shaped” -collection sites filled with phagocytes
a. 99% of the antigens will be removed by lymph node
2. Spleen – largest collection of lymphatic tissue(detects foreign substances), blood reservoir recycle center – macrophages engulf debris
a. Red pulp – remove abnormal or past prime RBC’s and recycle iron
b. White pulp – immune response - lymphoid nodules – microphages, stimulated by foreign antigens
3. Thymus – max size by about age 1- decreases size in older adults
a. Site of T cell maturation –mature in the cortex, migrate to the medulla and enter blood vessels
b. Thymic hormone production (thymosins)= maturation of T cells - (cell-mediated immunity)
4. Lymphatic Nodules- Mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT) - protect pharynx from pathogens entering nasal/oral cavities
a. Tonsils - Pharyngeal tonsil – adenoid tonsils - Palatine tonsils = “The tonsils” -most removed are the lingual tonsils.
5. Bone Marrow - Found inside several long bones, the sternum, and pelvis. All blood cells are produced in the bone marrow including B- and T-lymphocytes of the immune system
1. Lymphatic vessels – carry lymph, contain one way valves – very low pressure
a. Lymphatic capillaries blind pockets endothelial cells, prevent backflow into intercellular spaces
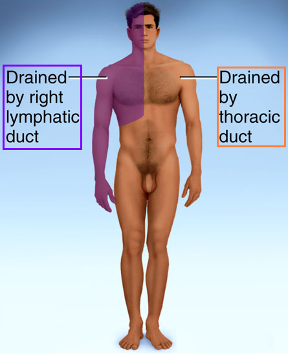
b. Thoracic duct drains lower abdomen & pelvis, left half of head, neck & chest, empties into left subclavian and left jugular vein.
c. Right lymphatic duct – Drains the right side of body above diaphragm
2. Fluid – moved by skeletal muscle pump and the respiratory pump. 3.6L/day – eliminates local variations in the composition of interstitial fluid.
1. Drain excess interstitial fluid - 3.6L/day – eliminates local variations in the composition of interstitial fluid. 30L of fluid/day from capillaries →interstitial tissues. 27 L of fluid/day from interstitial tissues →capillaries
2. Transport dietary lipids - lacteals lymphatic vessels in small intestine
3. Carry out immune responses – destroy foreign invaders
This website touches on all aspects of the Lymphatic System.